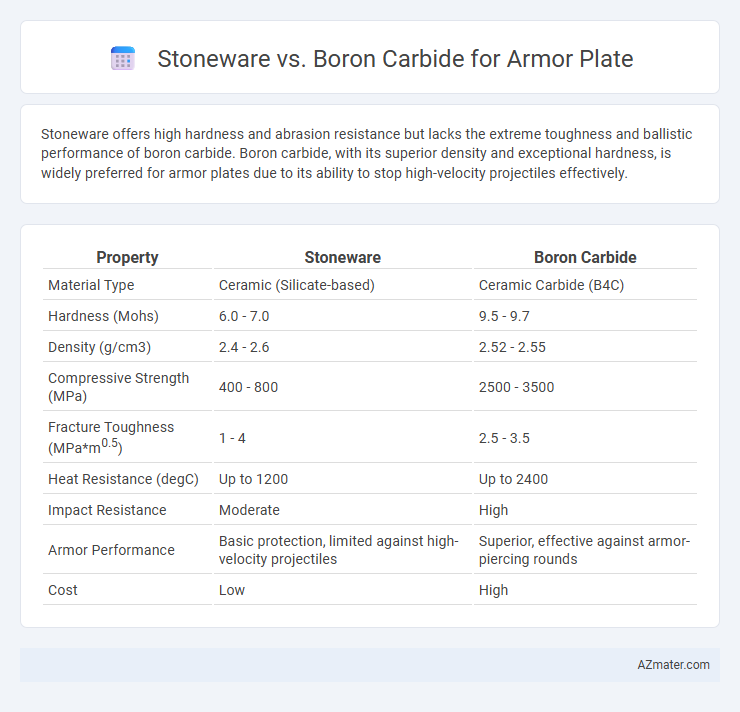
Stoneware offers high hardness and abrasion resistance but lacks the extreme toughness and ballistic performance of boron carbide. Boron carbide, with its superior density and exceptional hardness, is widely preferred for armor plates due to its ability to stop high-velocity projectiles effectively.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Boron Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic (Silicate-based) | Ceramic Carbide (B4C) |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.0 - 7.0 | 9.5 - 9.7 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.4 - 2.6 | 2.52 - 2.55 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 400 - 800 | 2500 - 3500 |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa*m0.5) | 1 - 4 | 2.5 - 3.5 |
| Heat Resistance (degC) | Up to 1200 | Up to 2400 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Armor Performance | Basic protection, limited against high-velocity projectiles | Superior, effective against armor-piercing rounds |
| Cost | Low | High |
Introduction to Armor Plate Materials
Stoneware offers cost-effective hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for low-velocity impact armor applications. Boron carbide excels with an exceptional combination of ultra-high hardness, low density, and superior ballistic protection, ideal for advanced body armor and military-grade plates. Material selection depends on balancing durability, weight, and threat level to optimize armor performance.
Overview of Stoneware in Armor Applications
Stoneware armor plates offer robust ballistic protection due to their high hardness and fracture toughness, effectively dissipating impact energy from projectiles. Their ceramic composition provides resistance to wear and environmental degradation, making them suitable for long-term use in harsh conditions. Although heavier than advanced ceramics like boron carbide, stoneware materials deliver cost-effective and reliable armor solutions for military and security applications.
Boron Carbide: Properties and Advantages
Boron carbide armor plates exhibit exceptional hardness, ranking just below diamond on the Mohs scale, which provides superior ballistic protection against high-velocity projectiles. The material's low density of approximately 2.52 g/cm3 contributes to lightweight armor solutions, enhancing mobility without compromising durability. Its excellent resistance to abrasion, chemical corrosion, and high-temperature stability makes boron carbide ideal for military and personal protective armor applications.
Comparative Hardness and Strength
Stoneware exhibits moderate hardness and durability, making it suitable for general-purpose armor applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial. Boron carbide, possessing exceptional hardness--ranking just below diamond on the Mohs scale--and superior compressive strength, offers enhanced ballistic resistance and impact toughness for advanced armor plates. The comparative strength of boron carbide significantly outperforms stoneware, providing lightweight protection capable of stopping high-velocity projectiles with minimal material thickness.
Weight Considerations for Body Armor
Boron carbide armor plates offer superior weight advantages compared to traditional stoneware, making them ideal for mobile body armor applications. While stoneware plates tend to be heavier and bulkier due to their ceramic composition, boron carbide provides a higher strength-to-weight ratio, resulting in lighter, more comfortable protective gear. This weight reduction significantly enhances soldier endurance and mobility without compromising ballistic protection.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Stoneware exhibits moderate ballistic protection with high hardness but is prone to brittleness and cracking under impact, limiting its effectiveness against high-velocity projectiles. Boron carbide armor plates demonstrate superior ballistic performance due to their exceptional hardness-to-weight ratio, enabling them to absorb and dissipate energy efficiently while maintaining lightweight characteristics. This makes boron carbide the preferred material for advanced ballistic armor systems requiring enhanced multi-hit resistance and lower weight.
Durability and Longevity Under Fire
Boron carbide armor plates exhibit superior durability and longevity under fire due to their exceptional hardness and resistance to high-velocity impacts, outperforming stoneware materials which tend to fracture or chip more easily. Stoneware plates, while cost-effective, often lack the resilience necessary for sustained ballistic protection, as their ceramic composition is more brittle and prone to degradation over time under repeated stress. Boron carbide's lightweight and high fracture toughness make it a preferred choice for durable armor plating in military and tactical applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Stoneware armor plates offer a cost-effective alternative with moderate durability and wider availability in commercial markets, making them accessible for budget-conscious applications. Boron carbide armor plates, while significantly more expensive, provide superior hardness and lightweight protection, often reserved for high-performance military or tactical uses. The choice between stoneware and boron carbide hinges on balancing cost constraints with the required level of ballistic protection and material availability.
Suitability for Military and Civilian Use
Stoneware armor plates offer affordability and resistance to blunt impacts, making them suitable for civilian applications like personal body armor and lightweight protection. Boron carbide plates provide superior hardness and exceptional ballistic resistance, meeting stringent military standards for enhanced protection against armor-piercing rounds. The choice depends on the required threat level, with boron carbide preferred for frontline military use and stoneware adequate for lower-risk civilian environments.
Future Trends in Advanced Armor Materials
Future trends in advanced armor materials emphasize the integration of boron carbide due to its superior hardness, lightweight properties, and exceptional ballistic performance compared to traditional stoneware. Researchers are exploring nanostructured boron carbide composites and hybrid armor systems to enhance multi-hit resistance and reduce overall weight in military and civilian applications. Innovations in manufacturing techniques such as additive manufacturing and advanced sintering are expected to further optimize boron carbide's structural integrity and cost-effectiveness in next-generation armor plates.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Boron Carbide for Armor Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com