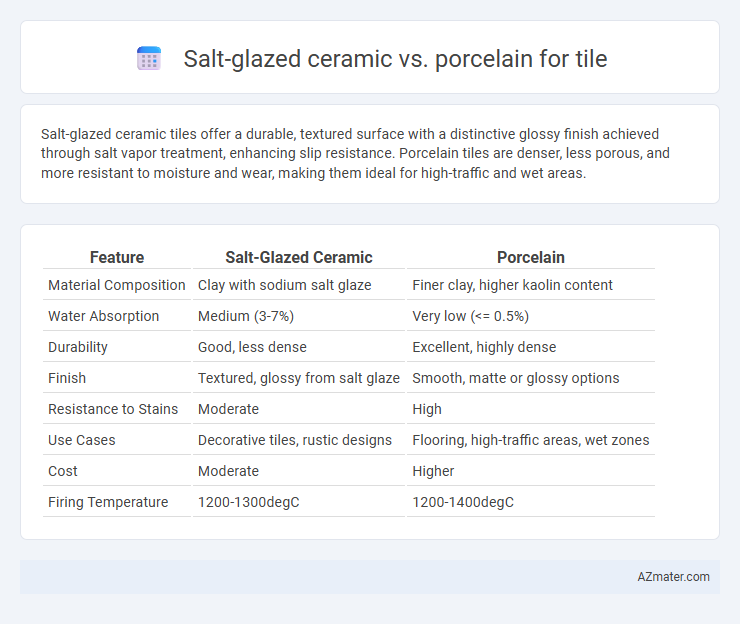
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles offer a durable, textured surface with a distinctive glossy finish achieved through salt vapor treatment, enhancing slip resistance. Porcelain tiles are denser, less porous, and more resistant to moisture and wear, making them ideal for high-traffic and wet areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay with sodium salt glaze | Finer clay, higher kaolin content |
| Water Absorption | Medium (3-7%) | Very low (<= 0.5%) |
| Durability | Good, less dense | Excellent, highly dense |
| Finish | Textured, glossy from salt glaze | Smooth, matte or glossy options |
| Resistance to Stains | Moderate | High |
| Use Cases | Decorative tiles, rustic designs | Flooring, high-traffic areas, wet zones |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC | 1200-1400degC |
Understanding Salt-Glazed Ceramic Tiles
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles feature a unique glassy surface created during high-temperature firing when salt vapor reacts with the clay body, producing a durable, slightly textured finish ideal for rustic or traditional aesthetics. This glazing technique enhances water resistance and surface hardness, making salt-glazed tiles suitable for high-moisture areas such as bathrooms and kitchens, though they typically exhibit more porosity than porcelain tiles. Compared to porcelain, salt-glazed ceramics offer a distinctive appearance with natural variations in glaze thickness, while porcelain tiles provide superior density, lower water absorption rates below 0.5%, and greater mechanical strength, making porcelain the preferred choice for commercial or high-traffic flooring applications.
What Is Porcelain Tile?
Porcelain tile is a dense, highly durable ceramic tile made from fine clay fired at higher temperatures compared to salt-glazed ceramics, resulting in a low-porosity, water-resistant surface ideal for flooring and walls. Unlike salt-glazed ceramic tiles, which have a characteristic glossy, textured finish created by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, porcelain tiles offer a smooth, uniform appearance with exceptional strength and minimal absorption rates. These properties make porcelain tiles more suitable for high-traffic areas and wet environments, providing superior longevity and stain resistance.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles undergo a unique manufacturing process where salt is introduced into the kiln at high temperatures, reacting with the silica in the clay body to form a glassy, textured surface. Porcelain tiles are produced using highly refined clay and fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a denser, less porous material with a smooth and uniform finish. The key manufacturing difference lies in the salt glazing technique that creates a distinctive glossy and textured surface for ceramics, while porcelain's vitrification process emphasizes durability and water resistance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles exhibit a hard, glass-like surface achieved through high-temperature firing with salt vapors, providing excellent resistance to abrasion and moderate durability suitable for wall applications. Porcelain tiles, composed of denser, finer clay fired at even higher temperatures, offer superior strength, lower porosity, and enhanced resistance to moisture and heavy foot traffic, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor flooring. The robust molecular structure and low water absorption rate of porcelain contribute to its greater durability and longevity compared to salt-glazed ceramics.
Water Resistance: Salt-Glazed vs Porcelain
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles exhibit superior water resistance due to their dense, glass-like salt glaze surface that minimizes moisture absorption and reduces the risk of water damage. Porcelain tiles, known for their low porosity and high density, also offer excellent water resistance but rely on their fine, compact body rather than a surface coating. For applications requiring maximum water resistance, salt-glazed ceramics provide robust protection through their impermeable glaze, while porcelain delivers durability through its intrinsic material properties.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finish
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles exhibit a distinctive textured surface with a natural, glossy sheen resulting from the high-temperature salt vapor reaction, creating an artisanal, rustic aesthetic ideal for vintage or farmhouse styles. Porcelain tiles offer a smooth, fine-grain finish with exceptional uniformity and a wider range of polished, matte, or satin surface options, making them versatile for modern, minimalist, or contemporary designs. The dense, non-porous surface of porcelain ensures superior scratch resistance and stain repellency compared to the more porous and slightly uneven finish of salt-glazed ceramics.
Installation Methods and Requirements
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles typically require a more flexible adhesive due to their textured surface and slight dimensional variations, which help accommodate expansion and contraction during installation. Porcelain tiles demand a thicker bed mortar or specialized thin-set adhesive because of their dense, non-porous structure, ensuring strong adhesion and preventing cracking. Proper substrate preparation is crucial for both, with porcelain often necessitating a more level and stable base to support its rigidity and weight.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles feature a textured surface that can trap dirt, requiring gentle scrubbing with non-abrasive cleaners and regular sealing to prevent stains. Porcelain tiles offer a denser, smoother surface, making them more resistant to moisture and easier to clean with standard tile cleaners without special maintenance. Both tile types benefit from routine sweeping and prompt spill cleanup, but porcelain's low porosity significantly reduces the risk of mold and discoloration compared to salt-glazed ceramic.
Cost Implications of Each Tile Type
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to porcelain due to lower manufacturing costs and less dense material composition. Porcelain tiles, known for their durability and water resistance, often come with higher price points reflecting the complex production process and superior material quality. Homeowners should weigh the initial investment against the longevity and maintenance costs, as porcelain may reduce long-term expenses despite the higher upfront cost.
Choosing the Right Tile for Your Space
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles offer a rustic, textured finish with enhanced durability and moisture resistance, making them ideal for outdoor and high-traffic areas. Porcelain tiles, characterized by their dense, fine-grained composition and low water absorption rate, excel in both indoor and wet environments with a sleek, polished appearance. Selecting the right tile depends on balancing aesthetic preferences with functional needs such as wear resistance, slip resistance, and maintenance requirements for your specific space.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Porcelain for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com