Salt-glazed ceramic offers a durable, textured surface with a characteristic glossy finish created by salt vapor during firing, enhancing its rustic charm for decorative plates. Majolica features a brightly colored, tin-glazed surface that provides vibrant, intricate designs with a smooth, glossy texture ideal for ornamental display.
Table of Comparison
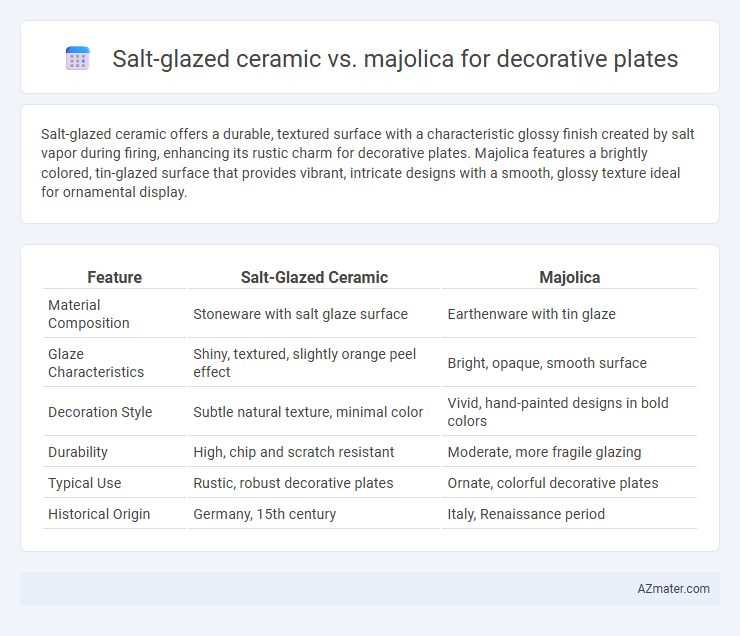
| Feature | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Majolica |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Stoneware with salt glaze surface | Earthenware with tin glaze |
| Glaze Characteristics | Shiny, textured, slightly orange peel effect | Bright, opaque, smooth surface |
| Decoration Style | Subtle natural texture, minimal color | Vivid, hand-painted designs in bold colors |
| Durability | High, chip and scratch resistant | Moderate, more fragile glazing |
| Typical Use | Rustic, robust decorative plates | Ornate, colorful decorative plates |
| Historical Origin | Germany, 15th century | Italy, Renaissance period |
Introduction to Decorative Plates: Salt-Glazed vs Majolica
Salt-glazed ceramic decorative plates feature a distinctive glossy surface created by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, resulting in a durable, textured finish prized for its rustic charm and subtle color variations. Majolica plates are known for their vibrant, tin-glazed surfaces with intricate painted designs, offering a smooth, colorful appearance that highlights detailed artistry and historical motifs. Choosing between salt-glazed and majolica decorative plates depends on preferences for texture and durability versus vibrant color and intricate decoration.
Historical Origins of Salt-Glazed Ceramics
Salt-glazed ceramics trace their origins to 15th-century Germany, where potters introduced salt into the kiln at high temperatures, producing a distinctive glossy, textured surface. This technique, characterized by its durable, slightly orange-peel finish, contrasts with the vibrant, tin-glazed Majolica pottery that emerged in Renaissance Italy. The historic salt glazing method not only enhanced functionality but also influenced European stoneware traditions, setting it apart from the more colorful and ornamental Majolica decorative plates.
The Art and Legacy of Majolica Pottery
Majolica pottery, renowned for its vibrant tin-glazed surface and intricate painted designs, represents a rich artistic legacy distinct from the more rustic, textured finish of salt-glazed ceramics. The art of Majolica involves applying a white glaze that serves as a canvas for colorful motifs, often inspired by Renaissance and Baroque themes, making it highly prized for decorative plates. Collectors and artisans value Majolica for its historical significance, detailed craftsmanship, and ability to combine both functional and ornamental qualities in ceramic art.
Materials and Production Techniques Compared
Salt-glazed ceramics are made by throwing salt into a hot kiln, causing a glassy, textured surface formed from a chemical reaction between salt and silica in the clay, typically using stoneware clay. Majolica plates use a tin-glazed earthenware technique where a white, opaque glaze is applied before hand-painting vibrant designs, requiring a two-step firing process to fix the glaze and colors. The salt-glaze method results in a durable, textured finish ideal for rustic styles, whereas Majolica offers smooth, glossy surfaces prized for detailed, colorful decorations.
Visual Characteristics: Texture and Color Differences
Salt-glazed ceramics feature a distinctive orange-peel texture with a glossy, translucent finish created by salt vapor reacting with the clay surface, resulting in subtle earth tones like gray, brown, and blue. In contrast, Majolica plates are known for their smooth, opaque tin-glazed surfaces with bright, vibrant colors and intricate hand-painted designs, often showcasing floral or geometric patterns. The tactile contrast between the rough, textured glaze of salt-glaze pottery and the sleek, glassy finish of Majolica highlights their unique decorative appeal.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Salt-glazed ceramic offers high durability due to its dense, glass-like surface that resists scratches and stains, making it ideal for long-term decorative plates requiring minimal upkeep. Majolica, characterized by its porous earthenware body covered with a tin glaze, is more susceptible to chipping and moisture absorption, necessitating careful handling and regular maintenance to preserve its vibrant colors. Choosing salt-glazed ceramics ensures easier cleaning and durability, while Majolica demands gentle care to maintain its artistic appeal.
Artistic Styles and Design Versatility
Salt-glazed ceramics feature a distinctive textured surface with earthy tones created by the salt vapor reaction during firing, lending a rustic and timeless artistic style ideal for traditional or minimalist decorative plates. Majolica, characterized by its vibrant tin-glazed surface and intricate, colorful patterns, offers exceptional design versatility that enables artists to incorporate detailed motifs ranging from floral to narrative scenes. The choice between salt-glazed ceramics and majolica for decorative plates depends on the desired aesthetic impact, with salt glaze emphasizing subtle, organic textures, while majolica excels in bold, vivid visual storytelling.
Cultural Significance and Collectibility
Salt-glazed ceramic plates, originating from 15th-century Germany, feature a distinctive glossy, textured surface created by introducing salt into the kiln, reflecting rustic European pottery traditions valued for their durability and historical authenticity. Majolica plates, rooted in Renaissance Italy and characterized by vibrant, tin-glazed surfaces with intricate hand-painted motifs, symbolize artistic expression and cultural storytelling, making them highly sought after by collectors for their vivid colors and elaborate designs. Collectibility of salt-glazed ceramics often appeals to enthusiasts of traditional, utilitarian craftsmanship, while Majolica's ornate and colorful aesthetic attracts collectors focused on European decorative arts and ornate heritage pieces.
Price Points and Accessibility in the Market
Salt-glazed ceramics generally have a higher price point due to their labor-intensive production process and durability, making them less accessible to casual buyers. Majolica decorative plates are more widely available and often more affordable, benefiting from mass production and vibrant, colorful glazes that appeal to a broader market. Collectors seeking unique, artisanal pieces may lean toward salt-glazed options, while budget-conscious buyers often prefer the easier accessibility and lower cost of Majolica.
Choosing the Right Ceramic for Your Decorative Plate
Salt-glazed ceramics offer a durable, textured finish ideal for rustic or traditional decorative plates, providing natural variations in color and a glossy surface resistant to scratches. Majolica, known for its vibrant, colorful glazes and intricate hand-painted designs, excels in creating visually striking plates perfect for display in artistic or classic settings. Choosing the right ceramic depends on the desired aesthetic, durability needs, and whether the plate is intended primarily for decoration or light use.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Majolica for Decorative Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com