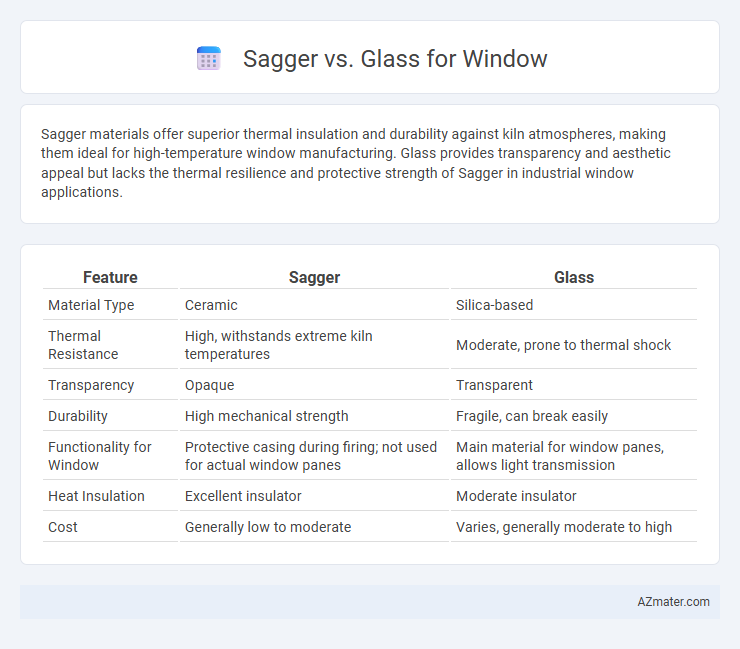
Sagger materials offer superior thermal insulation and durability against kiln atmospheres, making them ideal for high-temperature window manufacturing. Glass provides transparency and aesthetic appeal but lacks the thermal resilience and protective strength of Sagger in industrial window applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sagger | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic | Silica-based |
| Thermal Resistance | High, withstands extreme kiln temperatures | Moderate, prone to thermal shock |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Fragile, can break easily |
| Functionality for Window | Protective casing during firing; not used for actual window panes | Main material for window panes, allows light transmission |
| Heat Insulation | Excellent insulator | Moderate insulator |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Varies, generally moderate to high |
Introduction to Sagger and Glass for Windows
Sagger is a heat-resistant ceramic container used in glass manufacturing to shape and support molten glass during the forming process, ensuring precise window dimensions and quality. Glass for windows, commonly made from soda-lime silica, offers transparency, durability, and thermal insulation essential for building applications. The interaction between sagger design and glass composition directly affects the clarity, strength, and defect-free surface of the finished window pane.
Defining Sagger: What Is It?
A sagger is a refractory container used in high-temperature furnace processes to protect fragile materials such as glass or ceramics from direct flame and contamination during firing. It provides a controlled environment that prevents deformation, oxidation, and other damage by isolating the workpiece. Unlike window glass, which serves as a transparent barrier primarily for insulation and visibility, a sagger functions as a protective enclosure to maintain the integrity of sensitive materials under extreme heat conditions.
Understanding Glass as a Window Material
Glass used in windows offers excellent transparency, thermal insulation, and durability, making it a preferred material for maximizing natural light and energy efficiency in buildings. Modern window glass types include tempered, laminated, and insulated varieties, each enhancing safety, soundproofing, and thermal performance. Innovations in glass coatings and treatments further improve resistance to UV rays, condensation, and weather impacts, optimizing comfort and longevity.
Key Differences Between Sagger and Glass
Sagger is a heat-resistant ceramic container designed to protect materials during high-temperature processes, while glass is a transparent, brittle material primarily used for windows to provide visibility and insulation. Unlike glass, which functions as a barrier to environmental elements with clarity, sagger serves as a protective vessel in industrial applications such as firing ceramics, preventing contamination and deformation. The key differences lie in their composition, purpose, and temperature resistance, with sagger excelling in durability under extreme heat and glass prioritizing transparency and rigidity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Sagger materials typically offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional glass, resisting high temperatures and mechanical stress without cracking. Glass windows, while providing clarity and aesthetic appeal, are more prone to shattering under impact and often require additional treatments for enhanced toughness. Sagger's robust nature makes it ideal for industrial or high-stress environments where longevity and resistance to damage are critical.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Sagger windows utilize advanced ceramic insulation materials that significantly reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. In contrast, glass windows rely heavily on double or triple glazing with inert gas fills to improve insulation but may still experience greater thermal conductivity compared to Sagger. Energy savings with Sagger windows can reach up to 30% more than standard glass models due to their superior thermal resistance and reduced heat gain or loss.
Cost Analysis: Sagger vs Glass
Saggers generally offer a more cost-effective solution for window manufacturing compared to glass, especially in high-temperature or specialized industrial applications where durability is crucial. The initial investment in saggers includes material and manufacturing costs but reduces long-term expenses due to higher thermal resistance and lower breakage rates, minimizing maintenance and replacement needs. Conversely, glass entails higher upfront costs and greater vulnerability to thermal shock, which can lead to increased operational expenditure over time despite its optical clarity advantages.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Glass windows offer superior aesthetic appeal with their clarity and ability to reflect natural light, creating bright, open spaces ideal for modern architectural designs. Sagger, made from terracotta or clay, provides a unique textured finish and earthy tones that enhance rustic or traditional aesthetics, adding warmth and character. Design flexibility is greater with glass due to its varied transparency options, shapes, and integration with smart technologies, while Sagger excels in customizable patterns and handcrafted details for bespoke, artisanal window treatments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sagger materials used for windows often involve high-temperature ceramics that require significant energy consumption during manufacturing, leading to a larger carbon footprint compared to glass. Glass windows, especially those made from recycled or low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, provide enhanced sustainability by reducing energy usage in production and improving building insulation, thereby lowering heating and cooling demands. Choosing glass over sagger aligns with eco-friendly construction goals due to better recyclability and reduced environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Windows
Selecting between sagger and glass for windows depends on durability, thermal insulation, and aesthetic preferences. Glass offers superior transparency, energy efficiency, and ease of maintenance, while sagger, typically ceramic or fire-resistant material, provides enhanced heat resistance and structural protection in industrial settings. For residential or commercial window applications prioritizing clarity and insulation, tempered or laminated glass is the optimal choice.
Infographic: Sagger vs Glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com