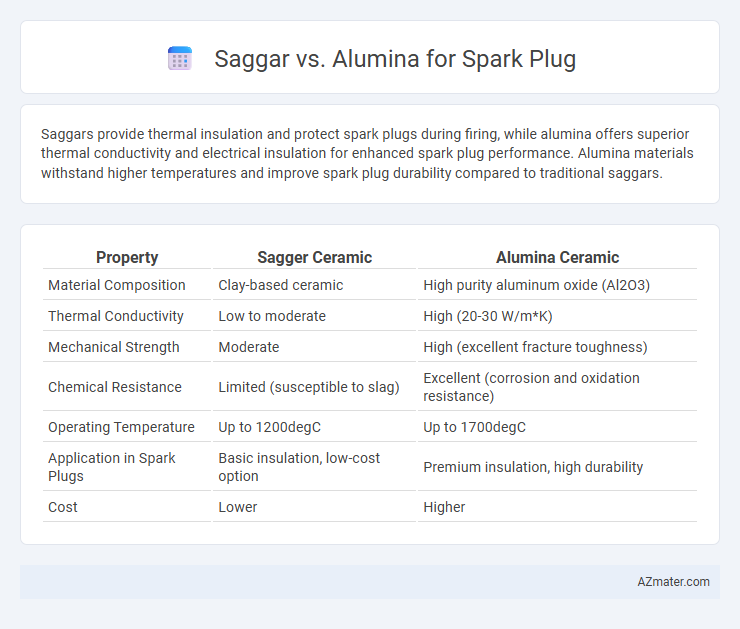
Saggars provide thermal insulation and protect spark plugs during firing, while alumina offers superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation for enhanced spark plug performance. Alumina materials withstand higher temperatures and improve spark plug durability compared to traditional saggars.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger Ceramic | Alumina Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-based ceramic | High purity aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate | High (20-30 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High (excellent fracture toughness) |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited (susceptible to slag) | Excellent (corrosion and oxidation resistance) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1700degC |
| Application in Spark Plugs | Basic insulation, low-cost option | Premium insulation, high durability |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Spark Plug Insulators
Spark plug insulators primarily use sagger or alumina materials to ensure optimal electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. Alumina (Al2O3) is favored for its excellent dielectric strength, high thermal stability, and resistance to corrosion, improving spark plug durability and performance. Saggers, typically ceramic molds, influence the microstructure of alumina insulators, enhancing mechanical strength and consistency during manufacturing.
Overview of Sagger and Alumina Materials
Sagger and alumina materials are critical components in spark plug manufacturing, each offering distinct properties that influence performance and durability. Sagger, typically a refractory ceramic used for protective packaging during firing, provides thermal insulation and chemical stability, preventing contamination of spark plugs during kiln processing. Alumina, a highly purified aluminum oxide, delivers exceptional electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength, making it the preferred ceramic dielectric material in spark plug insulators.
Material Composition and Properties
Sagger and alumina differ significantly in material composition, with Sagger typically composed of refractory clay materials, while alumina is a pure ceramic oxide (Al2O3) known for its high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. Alumina offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and temperature stability, making it ideal for spark plug insulators exposed to extreme combustion conditions. In contrast, saggers provide moderate thermal resistance but lack the electrical insulating properties and mechanical strength required for high-performance spark plug applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Sagger, used as a ceramic substrate in spark plugs, offers superior thermal conductivity compared to alumina, enabling more efficient heat dissipation and improved thermal performance. Alumina, known for its high dielectric strength and thermal stability, provides excellent insulation but lower thermal conductivity than Sagger, potentially leading to higher operating temperatures. Optimizing spark plug durability and heat management often involves balancing Sagger's enhanced thermal conductivity with alumina's insulation properties to suit specific engine operating conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Sagger material and alumina ceramic both play critical roles in spark plug manufacturing, with alumina exhibiting superior mechanical strength due to its high density and hardness, resulting in enhanced wear resistance and durability under extreme thermal cycles. Alumina's outstanding thermal shock resistance minimizes cracking and deformation during ignition, whereas sagger ceramics typically have lower fracture toughness, making them less durable in high-stress ignition environments. The enhanced mechanical properties of alumina contribute to longer spark plug lifespan and consistent performance in internal combustion engines.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Sagger and alumina materials differ significantly in electrical insulation capabilities for spark plugs, with alumina offering superior dielectric strength and thermal stability. Alumina's high resistivity and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make it ideal for maintaining reliable electrical insulation in spark plug environments. Sagger materials typically have lower insulation performance, which can compromise spark plug efficiency and durability under high voltage conditions.
Resistance to Corrosion and Wear
Sagger materials exhibit superior resistance to corrosion compared to alumina, due to their enhanced chemical stability under high-temperature combustion conditions. Alumina offers excellent wear resistance with high hardness and thermal conductivity, making it effective against mechanical erosion but more susceptible to corrosive degradation over time. Selecting the appropriate material hinges on balancing alumina's wear resistance with the sagger's robust corrosion protection for spark plug longevity.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
Sagger spark plugs offer enhanced cost-effectiveness due to their economical manufacturing process while maintaining reliable performance under standard driving conditions. Alumina spark plugs provide superior longevity and thermal conductivity, leading to extended service intervals and better resistance to fouling in high-performance engines. Choosing between sagger and alumina depends on balancing upfront costs with long-term durability demands specific to the vehicle's usage.
Manufacturing Considerations and Scalability
Sagger materials in spark plug manufacturing offer cost-effective thermal insulation but pose challenges in scalability due to fragility during mass production processes. Alumina provides superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, supporting consistent quality and easier scalability in high-volume manufacturing environments. The choice between sagger and alumina directly impacts production efficiency, yield rates, and long-term durability of spark plugs.
Choosing the Ideal Material for Spark Plug Efficiency
Sagger and alumina differ significantly in thermal conductivity and durability, making material choice crucial for spark plug efficiency. Alumina's superior electrical insulation and high thermal resistance enhance ignition performance and longevity, whereas sagger offers cost advantages but lower heat dissipation. Selecting alumina optimizes combustion stability and reduces electrode wear, leading to improved engine reliability and fuel efficiency.
Infographic: Sagger vs Alumina for Spark Plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com