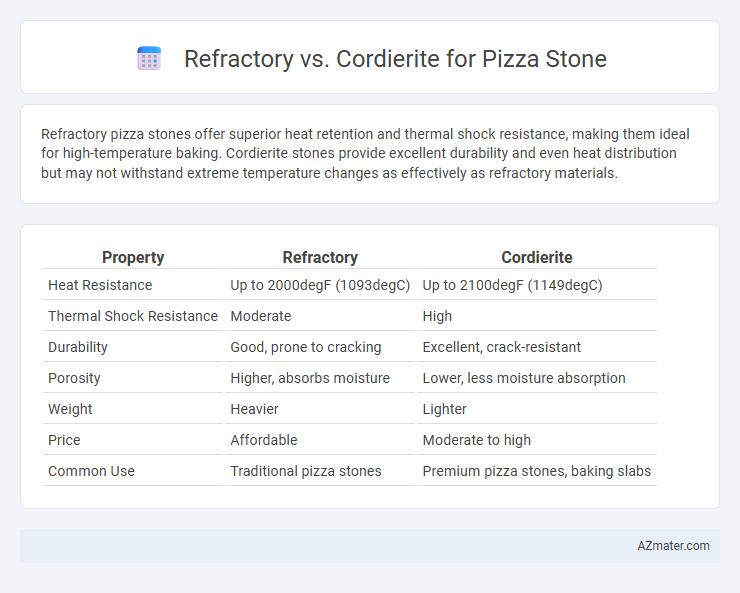
Refractory pizza stones offer superior heat retention and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature baking. Cordierite stones provide excellent durability and even heat distribution but may not withstand extreme temperature changes as effectively as refractory materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory | Cordierite |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 2000degF (1093degC) | Up to 2100degF (1149degC) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Good, prone to cracking | Excellent, crack-resistant |
| Porosity | Higher, absorbs moisture | Lower, less moisture absorption |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Price | Affordable | Moderate to high |
| Common Use | Traditional pizza stones | Premium pizza stones, baking slabs |
Introduction to Pizza Stones: Refractory vs. Cordierite
Pizza stones are essential tools for achieving crispy, evenly cooked crusts by retaining and distributing heat effectively. Refractory stones, made from high-temperature resistant materials like ceramic or fireclay, offer superior heat retention and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for intense baking environments. Cordierite stones, composed of a mineral known for durability and resistance to cracking, provide excellent heat conductivity and are popular for their lightweight nature and ease of maintenance in everyday pizza baking.
Material Composition: Understanding Refractory and Cordierite
Refractory pizza stones are typically made from high-temperature resistant materials like fireclay or ceramic blends that can withstand extreme heat without cracking or warping. Cordierite stones feature a crystalline mineral structure known for excellent thermal shock resistance, making them highly durable during rapid temperature changes. Understanding these material compositions helps determine the best pizza stone for even heat distribution and long-lasting performance.
Heat Retention and Distribution Comparison
Refractory pizza stones excel in heat retention due to their dense composition, maintaining high temperatures for longer baking sessions, which is ideal for achieving crispy crusts. Cordierite, known for its superior thermal shock resistance, offers even heat distribution that minimizes hot spots and ensures consistent cooking results. While refractory stones hold heat well, cordierite stones balance heat retention with excellent durability and uniform temperature spread, making them favorable for versatile baking conditions.
Durability and Lifespan: Which Lasts Longer?
Refractory pizza stones, often made from firebrick or high-temperature refractory clay, offer superior durability and can withstand extreme heat cycles without cracking, resulting in a longer lifespan compared to cordierite stones. Cordierite, although highly heat resistant and less prone to thermal shock than traditional ceramic, tends to wear down faster with regular use and may develop cracks over time under intense temperature fluctuations. For longevity and sustained performance, refractory materials generally outlast cordierite, making them a preferred choice for heavy-duty pizza baking.
Temperature Tolerance: High-Heat Performance
Refractory pizza stones exhibit exceptional temperature tolerance, comfortably withstanding temperatures upwards of 1200degF, making them ideal for traditional wood-fired ovens and intense heat environments. Cordierite stones, while slightly less heat-resistant, can still tolerate temperatures around 950degF to 1000degF, offering excellent thermal shock resistance that minimizes cracking risk. Both materials ensure high-heat performance but refractory stones provide superior durability for extreme baking conditions.
Cooking Results: Crust Texture and Taste Differences
Refractory pizza stones offer superior heat retention and distribution, resulting in a crispier, evenly baked crust with a slightly smoky flavor that enhances the pizza's overall taste. Cordierite stones, known for their thermal shock resistance, provide a more moderate heat transfer, producing a crust that is tender yet firm, often preserving more of the dough's natural moisture and subtle flavors. Choosing between refractory and cordierite stones significantly impacts crust texture and taste, with refractory favoring crunch and caramelization, while cordierite emphasizes a balanced, chewy bite.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Refractory pizza stones demand more thorough maintenance due to their porous structure, requiring thorough drying before storage to prevent cracking and regular gentle scrubbing to avoid residue buildup. Cordierite stones offer easier cleaning with less absorption of moisture and food particles, allowing for simpler wiping or brushing without the risk of damage from water exposure. Both materials benefit from avoiding soap and soaking, but cordierite's durability and resistance to thermal shock make it more forgiving for everyday use and maintenance.
Price Point: Cost Analysis of Refractory vs. Cordierite
Refractory pizza stones generally come at a higher price point due to their superior heat retention and durability, often ranging from $50 to $150. Cordierite stones, known for their affordability and thermal shock resistance, typically cost between $20 and $60, making them a budget-friendly option for casual pizza makers. When weighing cost against performance, refractory stones offer long-term value through endurance, while cordierite stones present an accessible entry point without sacrificing essential cooking quality.
Best Use Cases: Home Ovens vs. Professional Pizzerias
Refractory pizza stones excel in professional pizzerias due to their ability to withstand extremely high temperatures and provide superior thermal shock resistance, ensuring consistent, artisanal-quality crusts in commercial ovens. Cordierite stones are ideal for home ovens, offering excellent heat retention and durability at lower temperatures, making them a practical choice for everyday pizza baking without risking cracking. Choosing between refractory and cordierite depends on oven type and usage frequency, with refractory suited for intense, high-volume heat and cordierite optimized for moderate, household cooking conditions.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Pizza Stone for You
Refractory stones offer superior heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for achieving a crispy crust in high-temperature pizza baking. Cordierite stones provide excellent thermal shock resistance, durability, and faster heat-up times, suitable for frequent use and versatility. Selecting the right pizza stone depends on your baking frequency, preferred crust texture, and oven temperature capabilities.
Infographic: Refractory vs Cordierite for Pizza Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com