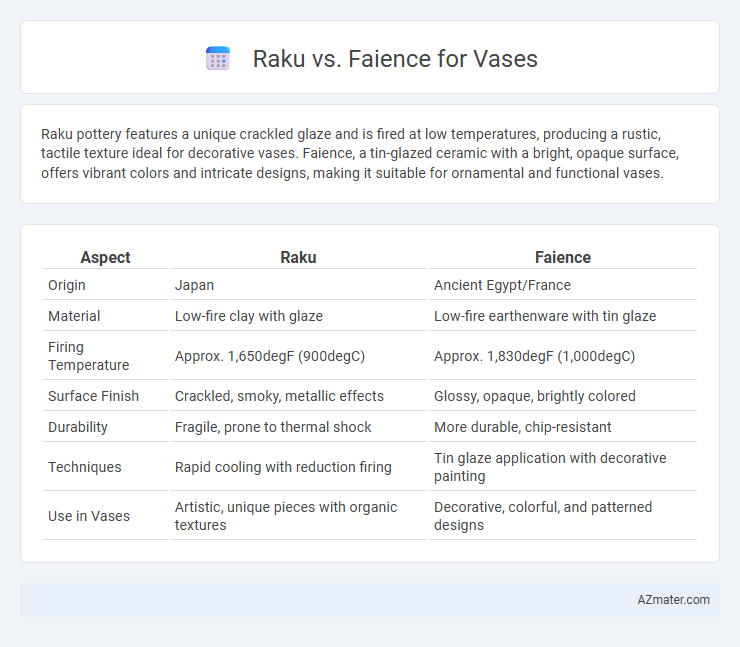
Raku pottery features a unique crackled glaze and is fired at low temperatures, producing a rustic, tactile texture ideal for decorative vases. Faience, a tin-glazed ceramic with a bright, opaque surface, offers vibrant colors and intricate designs, making it suitable for ornamental and functional vases.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Raku | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Japan | Ancient Egypt/France |
| Material | Low-fire clay with glaze | Low-fire earthenware with tin glaze |
| Firing Temperature | Approx. 1,650degF (900degC) | Approx. 1,830degF (1,000degC) |
| Surface Finish | Crackled, smoky, metallic effects | Glossy, opaque, brightly colored |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to thermal shock | More durable, chip-resistant |
| Techniques | Rapid cooling with reduction firing | Tin glaze application with decorative painting |
| Use in Vases | Artistic, unique pieces with organic textures | Decorative, colorful, and patterned designs |
Introduction to Raku and Faience Ceramics
Raku ceramics originate from a Japanese pottery tradition characterized by low-firing temperatures and rapid cooling techniques, resulting in unique crackled glaze patterns and an organic, textured surface ideal for artistic vases. Faience ceramics, rooted in ancient Egyptian and Mediterranean cultures, feature tin-glazed earthenware known for vibrant, opaque colors and smooth, glossy finishes that enhance decorative vase designs. Both Raku and Faience offer distinct aesthetic qualities: Raku emphasizes natural, rustic beauty through thermal shock effects, while Faience showcases bright, durable glazes suitable for ornamental purposes.
Historical Origins: Raku vs Faience
Raku pottery originated in 16th-century Japan, deeply rooted in the Zen Buddhist tea ceremony, characterized by hand-shaped forms and rapid firing techniques that produce unique, crackled glazes. Faience dates back to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, renowned for its brightly colored, tin-glazed earthenware used primarily for decorative and ceremonial vases. These contrasting origins highlight Raku's emphasis on naturalistic imperfection and spontaneity, while Faience reflects early technological advancements in glazing and symbolic artistry.
Materials and Composition Differences
Raku pottery is characterized by its unique low-firing process using porous clay bodies, typically stoneware or earthenware, which allows rapid cooling and crackle effects in its glaze composition containing feldspar and quartz. Faience, on the other hand, is a non-clay ceramic material primarily composed of silica and alkali materials, often glazed with tin-opacified surfaces that produce a bright, opaque finish. The fundamental difference lies in Raku's organic clay matrix and thermal shock technique versus Faience's synthetic silica base and tin-glazed surface, impacting durability and aesthetic qualities of vases.
Firing Techniques Compared
Raku firing involves rapid heating and cooling, often removing the vase from the kiln while glowing hot and placing it in combustible materials, creating unique crackles and metallic lusters. Faience firing uses a low-temperature technique to fuse a glassy, often brightly colored glaze onto a porous ceramic body, resulting in a smooth, glossy surface without thermal shock effects seen in Raku. The critical difference lies in Raku's dynamic, unpredictable firing process versus Faience's controlled, glaze-focused kiln environment.
Visual Aesthetics and Surface Qualities
Raku vases showcase a distinctive, crackled glaze with metallic sheens and smoky textures achieved through rapid cooling techniques, creating an organic, unpredictable surface aesthetic. Faience vases feature vivid, opaque glazes with smooth, glossy finishes and vibrant colors, often incorporating intricate patterns inspired by ancient Egyptian and Mediterranean artistry. The tactile quality of Raku is rougher and more varied, while Faience surfaces are polished and uniform, emphasizing decorative detail and color saturation.
Durability and Functional Considerations
Raku vases, known for their porous and brittle nature due to rapid cooling techniques, tend to be less durable and more prone to cracks and chipping compared to faience vases. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material, offers superior durability and resistance to water, making it highly suitable for functional vases intended to hold fresh flowers or liquids. When selecting a vase for practical use, faience provides enhanced structural integrity and long-term usability over the more fragile, decorative raku option.
Artistic Flexibility and Styles
Raku pottery offers artists exceptional artistic flexibility with its unpredictable firing process that creates unique crackles and metallic effects, ideal for expressive and spontaneous styles. Faience vases feature vibrant, opaque glazes and intricate painted designs, suited to precise, decorative artistry rooted in ancient traditions. Both mediums provide distinct aesthetic opportunities: Raku emphasizes organic, one-of-a-kind textures, while Faience showcases bold colors and detailed patterns.
Common Uses in Vase Making
Raku pottery is favored for vases due to its unique firing technique that creates crackled glazes and organic textures, ideal for decorative and artistic pieces. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic, is commonly used for sturdy, colorful vases with a glossy finish, often found in historic and ornamental designs. Both materials serve distinct aesthetic and functional purposes in vase making, with Raku prized for its rustic appeal and Faience for vibrant, durable surfaces.
Cost and Accessibility of Each Method
Raku pottery often comes with higher costs due to the specialized firing process requiring a raku kiln and experienced hands, making it less accessible to beginners. Faience, meanwhile, is generally more affordable and accessible because it uses low-fired earthenware techniques and readily available materials. Artisans and hobbyists favor faience for budget-friendly production, while raku remains popular among collectors and professional studios seeking unique, iridescent finishes.
Choosing Between Raku and Faience for Vases
Choosing between Raku and Faience for vases depends on the desired aesthetic and technique. Raku vases feature unique crackled glazes and an organic, rustic finish achieved through rapid cooling in post-firing reduction, emphasizing texture and unpredictability. Faience vases showcase vibrant, opaque glazes with smooth surfaces and intricate patterns, reflecting an ancient glazing technique ideal for decorative elegance and fine detail.
Infographic: Raku vs Faience for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com