Porcelain insulators offer superior mechanical strength and weather resistance compared to glass, making them ideal for high-voltage applications and harsh environments. Glass insulators provide excellent electrical insulation and are easier to inspect for damage due to their transparency but are more fragile under mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
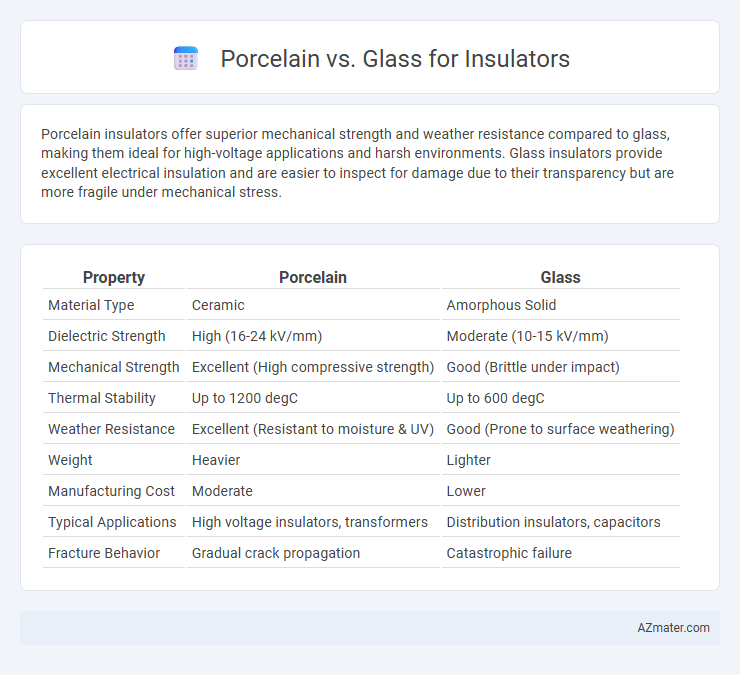
| Property | Porcelain | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic | Amorphous Solid |
| Dielectric Strength | High (16-24 kV/mm) | Moderate (10-15 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent (High compressive strength) | Good (Brittle under impact) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200 degC | Up to 600 degC |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent (Resistant to moisture & UV) | Good (Prone to surface weathering) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Manufacturing Cost | Moderate | Lower |
| Typical Applications | High voltage insulators, transformers | Distribution insulators, capacitors |
| Fracture Behavior | Gradual crack propagation | Catastrophic failure |
Introduction to Insulator Materials
Porcelain and glass are two primary materials used in the manufacturing of electrical insulators due to their excellent dielectric properties and mechanical strength. Porcelain insulators offer high resistance to weathering, mechanical stress, and electrical leakage, making them suitable for high-voltage applications. Glass insulators provide superior transparency, resistance to contamination, and self-cleaning properties, enhancing reliability in outdoor electrical systems.
Overview of Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators, made from high-strength ceramic materials, offer excellent mechanical durability and superior resistance to weathering and electrical stress compared to glass insulators. Their composition includes alumina and kaolin, which provide high dielectric strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-voltage power transmission. Porcelain insulators also provide enhanced resistance to pollution and thermal shocks, ensuring long service life in harsh outdoor environments.
Overview of Glass Insulators
Glass insulators offer superior electrical insulation and high mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-voltage power lines. Their non-porous surface resists contaminants and weathering, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs compared to porcelain. The inherent translucency of glass insulators allows for easier defect detection during inspections, contributing to improved reliability in power distribution systems.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Porcelain insulators are primarily composed of kaolin, quartz, and feldspar, fired at high temperatures to achieve a durable and hydrophobic ceramic structure that resists electrical leakage and environmental degradation. Glass insulators are made from silica sand, soda ash, and lime, which are melted and molded into a smooth, non-porous surface that offers excellent dielectric strength and UV resistance. The manufacturing process for porcelain involves kiln firing to create a dense, crystalline material, whereas glass insulators undergo controlled cooling to form a transparent, amorphous solid with consistent insulating properties.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Porcelain insulators exhibit higher dielectric strength and superior resistance to electrical stress, making them ideal for high-voltage applications compared to glass insulators. Glass insulators possess excellent electrical insulating properties with low leakage current due to their smooth surface, but they are more susceptible to mechanical failure under heavy electrical loads. The choice between porcelain and glass insulators depends on balancing dielectric performance, mechanical strength, and environmental factors to optimize electrical insulation efficiency.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to glass, with high compressive strength up to 700 MPa, making them ideal for heavy load applications. Glass insulators provide excellent durability through high resistance to surface erosion and weathering but are more brittle, prone to impact damage and lower tensile strength around 50 MPa. Porcelain's dense ceramic composition ensures enhanced longevity and resilience under mechanical stress, outperforming glass in environments subject to vibration and mechanical shock.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and pollution due to their dense ceramic structure and glaze coating, which prevent surface degradation and maintain high dielectric strength. Glass insulators, while offering excellent transparency and ease of inspection for cracks, are more susceptible to surface etching and contamination under harsh weather conditions, affecting long-term performance. Porcelain's ability to withstand extreme temperature variations and chemical exposure makes it the preferred choice for high-voltage outdoor electrical insulators.
Maintenance and Longevity
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior durability and require less frequent maintenance due to their robust ceramic composition, which resists weathering and electrical stress effectively. Glass insulators, while offering excellent visibility for detecting damage, may suffer from higher brittleness and potential for mechanical failure, increasing maintenance needs. Overall, porcelain insulators tend to provide longer service life and reduced upkeep costs in high-stress electrical environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Porcelain insulators generally offer higher durability and better resistance to weathering compared to glass insulators, often resulting in lower long-term maintenance costs despite their initially higher price. Glass insulators, while typically less expensive upfront and widely available, can be more brittle and prone to breakage, leading to potential replacement expenses that affect overall cost-effectiveness. Availability of glass insulators tends to be more consistent globally due to simpler manufacturing processes, whereas porcelain production may require specialized facilities and materials, impacting supply and pricing.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Porcelain insulators remain the preferred choice in high-voltage transmission lines and electrical substations due to their excellent mechanical strength, weather resistance, and superior electrical insulation properties. Glass insulators, favored in telecommunications and low to medium voltage power distribution, offer high visibility for defect detection, better thermal stability, and resistance to surface contamination. Industries prioritize porcelain in heavy-duty infrastructure projects while selecting glass insulators for applications requiring durability and ease of maintenance.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Glass for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com