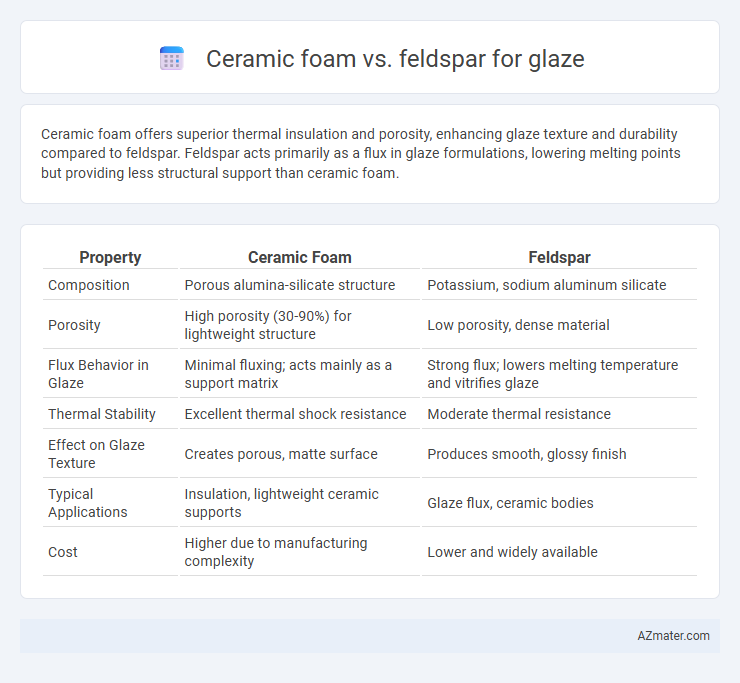
Ceramic foam offers superior thermal insulation and porosity, enhancing glaze texture and durability compared to feldspar. Feldspar acts primarily as a flux in glaze formulations, lowering melting points but providing less structural support than ceramic foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Foam | Feldspar |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Porous alumina-silicate structure | Potassium, sodium aluminum silicate |
| Porosity | High porosity (30-90%) for lightweight structure | Low porosity, dense material |
| Flux Behavior in Glaze | Minimal fluxing; acts mainly as a support matrix | Strong flux; lowers melting temperature and vitrifies glaze |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Effect on Glaze Texture | Creates porous, matte surface | Produces smooth, glossy finish |
| Typical Applications | Insulation, lightweight ceramic supports | Glaze flux, ceramic bodies |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing complexity | Lower and widely available |
Introduction to Ceramic Foam and Feldspar in Glaze Making
Ceramic foam serves as a highly porous material that enhances glaze texture and reduces weight, improving thermal insulation and durability. Feldspar, a key fluxing agent in glaze making, lowers melting temperature while contributing essential alumina and silica for hardness and chemical resistance. Combining ceramic foam and feldspar optimizes glaze performance by balancing porosity with structural integrity and glossy finish.
Composition Differences: Ceramic Foam vs Feldspar
Ceramic foam primarily consists of alumina, silica, and controlled porosity for lightweight structural applications, whereas feldspar is a natural aluminosilicate mineral rich in potassium, sodium, and calcium oxides used as a flux in glaze formulation. The high silica and alumina content in feldspar lowers the melting temperature and enhances glaze durability, while ceramic foam's composition is engineered for thermal insulation and mechanical strength rather than chemical fluxing. Feldspar's chemical composition directly influences glaze viscosity and surface finish, contrasting with ceramic foam's focus on physical properties rather than chemical reactivity in glaze development.
Role in Glaze Formulation
Ceramic foam acts primarily as a structural additive in glaze formulation, enhancing texture and surface properties by creating controlled porosity and reducing density. Feldspar serves as a crucial flux in glaze recipes, lowering the melting temperature and aiding in the formation of a smooth, glassy surface through its high potassium and sodium content. The combination of ceramic foam and feldspar optimizes glaze durability, appearance, and application performance by balancing structural integrity with melting behavior.
Effects on Glaze Texture and Surface
Ceramic foam creates a highly porous glaze surface, resulting in a textured, matte finish with increased tactile interest compared to feldspar. Feldspar acts primarily as a flux, producing a smooth, glossy surface with minimal texture by promoting glass formation during firing. Variations in foam concentration intensify surface roughness, while feldspar maintains consistent glaze fluidity and sheen.
Firing Temperatures and Thermal Stability
Ceramic foam typically demonstrates excellent thermal stability with firing temperatures ranging from 1200degC to 1450degC, making it suitable for high-temperature glaze applications. Feldspar, a common flux in ceramic glazes, melts at lower temperatures between 1100degC and 1350degC, promoting glass formation but offering less thermal stability compared to ceramic foam. The higher firing temperature tolerance of ceramic foam enhances its resistance to thermal shock and deformation, whereas feldspar's lower melting point affects the glaze's durability and firing range.
Color Outcomes and Visual Impact
Ceramic foam in glaze formulation enhances color depth and creates a matte, textured surface that intensifies light absorption for richer, darker hues. Feldspar contributes to a glossy, glass-like finish with brighter, more vivid colors due to its high flux content that promotes melting and smooth surface formation. The choice between ceramic foam and feldspar significantly influences the glaze's visual impact, where ceramic foam offers subtle, earthy tones and feldspar yields vibrant, glossy surfaces.
Durability and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Ceramic foam glazes exhibit superior durability and chemical resistance compared to feldspar-based glazes due to their highly porous structure and enhanced thermal shock absorption. Feldspar glazes, while widely used for their flux properties and smooth finish, tend to be more susceptible to acidic and alkaline corrosion over time. The porous network of ceramic foam contributes to better resistance against chemical wear, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring long-lasting surface protection.
Application Methods in Pottery and Ceramics
Ceramic foam glazes offer superior porosity and thermal insulation, making them ideal for advanced application methods such as spray coating and dipping in pottery, providing better control over layer thickness and texture. Feldspar, commonly used as a flux in glaze formulations, excels in traditional application techniques like brushing and pouring, ensuring consistent melting and glass formation during firing. The choice between ceramic foam and feldspar fundamentally affects glaze behavior, surface finish, and firing temperature requirements in ceramic production.
Cost and Availability for Artists
Ceramic foam offers high porosity and lightweight properties but tends to be more expensive and less readily available for artists compared to feldspar, which is abundant and cost-effective as a natural mineral flux in glaze formulations. Feldspar's widespread availability ensures consistent supply, making it a budget-friendly choice for large-scale or experimental glaze production. Cost constraints and local sourcing often drive artists to prefer feldspar despite ceramic foam's unique textural benefits.
Choosing Between Ceramic Foam and Feldspar for Optimal Results
Ceramic foam enhances glaze texture by increasing porosity and improving thermal insulation, making it ideal for lightweight, insulating coatings. Feldspar acts as a flux in glaze formulations, lowering the melting point and improving surface smoothness and durability. Selecting between ceramic foam and feldspar depends on whether the focus is on enhanced insulation and texture or on strength, melting behavior, and chemical stability for optimal glaze performance.
Infographic: Ceramic foam vs Feldspar for Glaze
 azmater.com
azmater.com