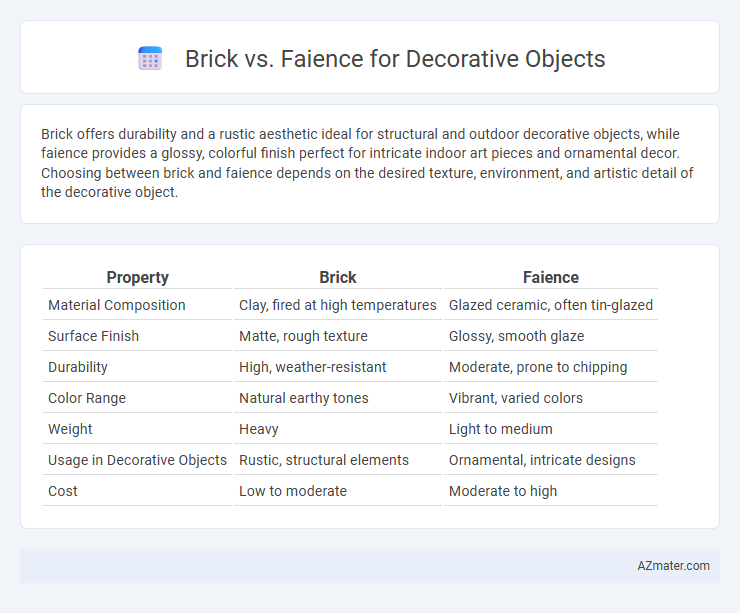
Brick offers durability and a rustic aesthetic ideal for structural and outdoor decorative objects, while faience provides a glossy, colorful finish perfect for intricate indoor art pieces and ornamental decor. Choosing between brick and faience depends on the desired texture, environment, and artistic detail of the decorative object.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay, fired at high temperatures | Glazed ceramic, often tin-glazed |
| Surface Finish | Matte, rough texture | Glossy, smooth glaze |
| Durability | High, weather-resistant | Moderate, prone to chipping |
| Color Range | Natural earthy tones | Vibrant, varied colors |
| Weight | Heavy | Light to medium |
| Usage in Decorative Objects | Rustic, structural elements | Ornamental, intricate designs |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Decorative Materials: Brick and Faience
Brick, a versatile and durable material composed of clay or shale, provides a textured, rustic aesthetic ideal for architectural and decorative objects. Faience, a glazed ceramic material rich in silica, offers vibrant colors and intricate patterns, frequently used in ancient and modern decorative arts. Both materials contribute unique visual and tactile qualities, with brick emphasizing earthy warmth and faience highlighting glossy, detailed ornamentation.
Historical Use of Brick and Faience in Art
Brick has been historically valued in architectural art for its durability and earthy aesthetics, prominently used in Mesopotamian ziggurats and Roman buildings to create robust decorative patterns. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic, was prized in ancient Egypt and the Near East for its vibrant colors and glossy finish, often fashioned into intricate jewelry, amulets, and small statuettes symbolizing spiritual protection. Both materials demonstrated cultural significance, with brick emphasizing structural artistry and faience showcasing ornamental sophistication in ancient decorative objects.
Material Composition and Properties
Brick, primarily composed of clay and fired at high temperatures, offers durability, thermal insulation, and a rustic texture ideal for architectural aesthetics. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material containing silica, alkali, and metallic oxides, provides a smooth, glossy finish with vibrant colors suitable for intricate decorative objects. The porous nature of brick contrasts with faience's glassy surface, influencing their respective resistance to moisture and aesthetic applications in interior and exterior design.
Aesthetic Qualities: Color, Texture, and Finish
Brick offers a warm, earthy palette with rich reds, browns, and oranges that evoke a rustic, natural charm, while faience provides vibrant, glossy finishes with a broad spectrum of colors ranging from deep blues to bright greens. The texture of brick is typically rough and porous, lending a tactile, rugged quality, contrasting with faience's smooth, glassy surface that reflects light and enhances visual depth. Finishing techniques on brick emphasize matte, aged appearances, whereas faience achieves high gloss and intricate glazing effects, making it ideal for striking decorative accents.
Durability and Longevity in Decorative Objects
Brick decorative objects exhibit superior durability due to their dense composition and resistance to weathering, making them ideal for long-term use in both indoor and outdoor settings. Faience, while prized for its vibrant glazed finish and intricate designs, tends to be more fragile and susceptible to chipping or fading over time, especially when exposed to environmental stressors. The longevity of brick as a decorative material often surpasses faience, offering sustained aesthetic appeal and structural integrity for architectural and ornamental applications.
Versatility in Design Applications
Brick offers robust structural versatility with its ability to form various shapes and sizes, making it ideal for both rustic and modern decorative objects. Faience excels in intricate detailing and vibrant glazing options, allowing for highly artistic and colorful embellishments in design applications. Combining these materials can enhance decorative objects by blending the durability of brick with the aesthetic appeal of faience.
Ease of Shaping and Customization
Brick offers moderate ease of shaping, typically requiring molds or cutting tools to achieve desired forms, making it less flexible for intricate designs compared to faience. Faience excels in customization due to its malleable clay base before firing, allowing artisans to create highly detailed and complex decorative objects with vibrant glazes. The smooth finish and fine texture of faience contribute to superior precision in shaping, making it ideal for ornamental and artistic pieces demanding fine craftsmanship.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Brick decorative objects require regular sealing to prevent stain absorption and facilitate easier cleaning, typically involving gentle scrubbing with mild soap and water to maintain their rustic look. Faience items, characterized by their glazed, non-porous surfaces, are more resistant to dirt and moisture, allowing for simpler maintenance using a soft cloth and non-abrasive cleaner to preserve their vibrant finish. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive tools to prevent surface damage and extend their decorative lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brick production requires significant energy and raw materials, contributing to higher carbon emissions compared to faience, which uses clay and glass-like materials fired at lower temperatures. Faience often incorporates recycled materials, making it more sustainable and reducing landfill waste. Choosing faience over brick minimizes environmental impact by lowering resource consumption and promoting circular economy practices in decorative objects.
Choosing Between Brick and Faience for Your Next Project
Choosing between brick and faience for your next decorative project depends largely on durability and aesthetic goals. Brick offers robust strength and rustic charm, making it ideal for outdoor or structural features, while faience provides intricate glazed finishes suited for detailed indoor applications. Evaluate environmental exposure and desired texture to ensure the material complements both design and functionality.
Infographic: Brick vs Faience for Decorative Object
 azmater.com
azmater.com